I know the transition from FTM doesn’t fall within the primary purpose of this blog, but I’ve always covered the technology of genealogy, and I think the FTM transition has been an important story in genealogy, and has a lot of interesting implications.
I previously reported on the retirement of FTM, what options were out there for transitioning away from FTM, and most recently about Ancestry’s selling of FTM to a third party (Software MacKiev) and licensing it’s APIs to another company (RootsMagic).
In my earliest post on the topic of FTM’s retirement, I mentioned a discontinued product called AncestorSync that had been created to move data between different genealogy programs and services. The need for something like AncestorSync existed (and still exists) because the only way to transfer data between genealogy programs and services has been to use a GEDCOM file, whose standard was last updated back in 1999. GEDCOM hasn’t evolved with genealogy programs, and because of that it cannot transfer everything we collect in our genealogy programs to another program or service without losing some data. Not every program or service interprets GEDCOM the same way either, which leads to other programs like data corruption.
This is why the FTM transition is so interesting. As if to prove how big of a problem all of the above is, we’ve seen multiple genealogy software companies modify their programs to better import GEDCOM files from FTM. So far GEDCOM is the only option available, but by the end of the year there will be the two options I recently mentioned – an updated FTM under new ownership, and a version of RootsMagic that can import FTM files directly. That two companies other than Ancestry will now have software capable of importing FTM files directly, is only because Ancestry no longer views these companies as competitors. Up until now, it wasn’t in Ancestry’s interest to allow any third-party company to be able to read the FTM file format other than themselves.
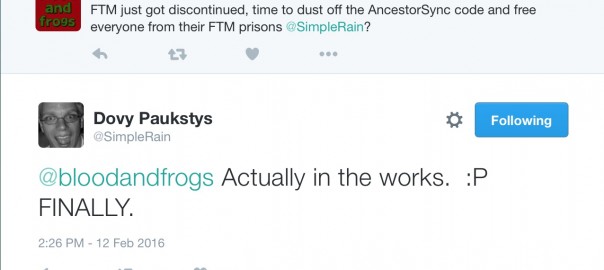
So we know have two groups of options for former FTM users. We have a slew of genealogy software companies that have updated their programs to better import FTM-generated GEDCOM files, and we have a second smaller group (pair) of companies that will be able to read FTM files directly. That brings us to the third possible option, which I mentioned way back in December, and again just up above – AncestorSync. Years ago when AncestorSync was being introduced I happened to meet the CTO of the company producing it, Dovy Paukstys. We were at a genealogy conference, and he was showing off his product. When FTM made their announcement, I fired off a tweet to Dovy, wondering if AncestorSync might be resurrected. AncestorSync fell off the radar two years ago, and Dovy had moved on to other things, but I figured he would know what happened to the technology.
Back in December I hadn’t heard a response, and didn’t think much about it until a couple of days ago when Dovy finally responded:
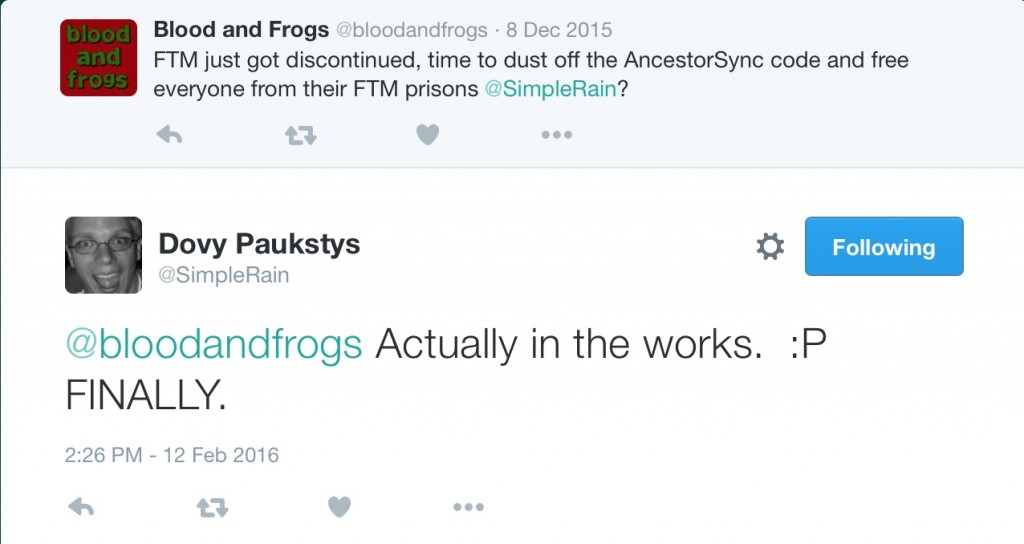
So it seems there might now be another option for FTM users on the way. The goal of AncestorSync, as I recall, was to allow the transfer of data between programs and services while retaining all the information. AncestorSync had modules for each program or service it supposed, and allowed you to move data around between the different modules. Initially the services and programs supported included Geni, MyHeritage, FamilySearch, ourFamilyology, Legacy Family Tree, RootsMagic, PAF, Ancestral Quest and FTM. I do remember work was underway on The Master Genealogist (since discontinued) and MacFamilyTree.
Of course, if a new standard were to emerge to replace GEDCOM, a program like AncestorSync wouldn’t be necessary. As efforts like GEDCOM X and FHISO haven’t yet managed to come up with a format that can handle better interchange of data and get it accepted by the genealogy software ecosystem, AncestorSync might yet fill the void.